In our latest paper we leveraged the anisotropic properties of curved sheets to create reconfigurable joints. Imagine a flat material like a thin piece of paper. This piece of paper can be stiffened by curving it along a single axis into a U-shape. In this case the anisotropic property is that it resists bending along the curve due to increased stiffness in the remaining axis. This stiffness can be reduced by creating a small change in shape along the curve such as creating a temporary flat spot or crease, which results in a reduced stiffness at that point meaning the curved paper can bend there.
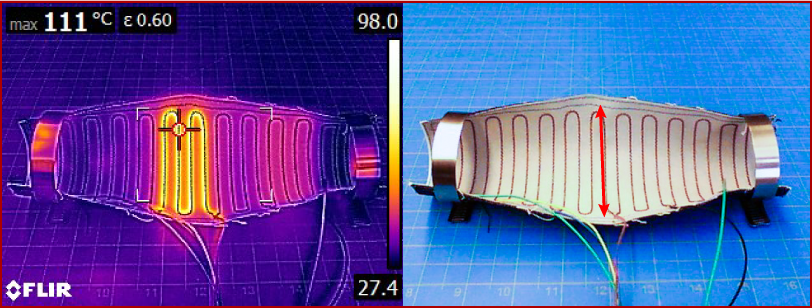
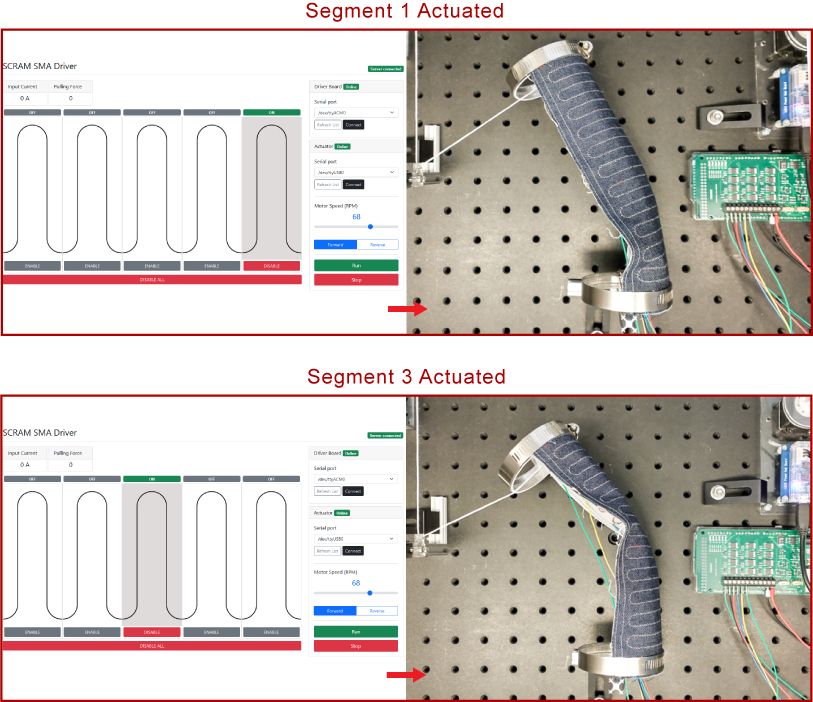
We used shape-memory alloy (SMA) wire sewn into some denim and stiff plastic using tailored wire placement to form a “crease” when energized which creates a flexure hinge, allowing the structure to bend. Since we are able to electronically control where this crease is formed we can create a hinge up and down the structure, meaning we can reconfigure the location of the joint.
Here’s the proceeding:
This project is part of the SCRAM consortium, supported by NSF award 1935324.